When ADHD Interferes With Your Relationships
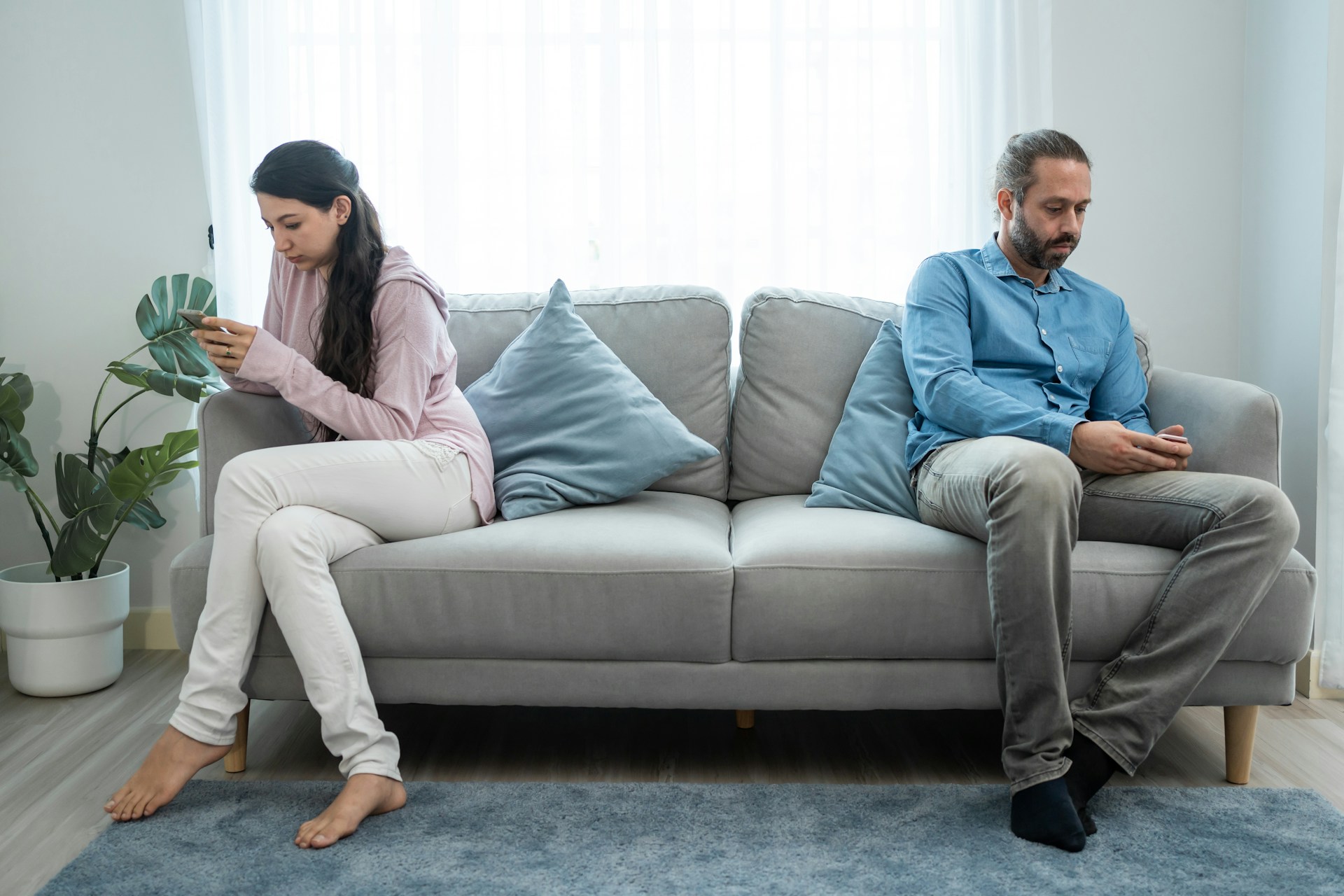
Relationships are important. They are part of God’s plan. He made us social creatures. In Genesis, we find that God didn’t want Adam to be alone, so He created Eve. The Bible is full of stories of how God has provided people to do his work and to love His followers. So, when you long for relationships, it’s not unusual – it’s part of God’s plan. But if you have attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (also known as ADHD), you may be struggling in your relationships. It’s one thing to desire deep, meaningful, and mutually beneficial relationships, and it’s a whole other thing to make and preserve them. ADHD Relationship Obstacles If you have ADHD, you’re probably already familiar with some of the obstacles that this disorder presents when it comes to interpersonal relationships. You’re probably acutely aware of the fact that you interrupt people when they’re talking or that you have a hard time focusing on a conversation. You probably cringe when you think about the time that you were pacing the floor acting disinterested in a conversation. But your mind and your body often follow the directions of ADHD rather than social norms. A romantic relationship adds a whole other layer of confusion and misunderstanding. You might be in a fully committed, loving relationship, ready to make a life together, but if your partner doesn’t understand your ADHD, you might not be perceiving the relationship in the same way. When you forget something they just said or lose track of the task that you promised to handle, it can feel to them like you’re careless or indifferent or even worse, that you simply don’t prioritize them or their needs. If they don’t understand that your brain works just a little differently, they may interpret your actions as lazy, [...]